David Walter
In any project, time is rarely negotiable. Deadlines are linked to budgets, contracts and stakeholder expectations, and even a small delay can disrupt the entire schedule. The real challenge is knowing which tasks truly control the final delivery date, especially when multiple activities are happening at the same time.
This is where the Critical Path Method (CPM) becomes essential. It helps determine the project’s completion date, providing better control over priorities, resources, and risks. In this blog, you will discover what is Critical Path Method in Project Management, how it works and how it can help you deliver projects on time. Let's dive in!
What is the Critical Path Method?
The Critical Path Method (CPM) is a Project Management technique used to identify the longest sequence of dependent tasks that determines the minimum time needed to complete a project. It is a step-by-step project scheduling and modelling process that focuses on mapping activities, estimating durations, and analysing dependencies of a project. By highlighting time-critical activities, CPM helps Project Managers prioritise work and manage schedules more effectively.
What is the Critical Path in Project Management?
In Project Management, the Critical Path refers to the specific sequence of activities within a project schedule that directly controls the project’s completion date. If any activity on this path is delayed, the overall project deadline will also be delayed. Tasks on the Critical Path typically have zero float or slack, meaning there is no flexibility for delay. Tasks outside the Critical Path may have some flexibility and can be postponed without affecting the final delivery date.
Why is the Critical Path Method Used in Project Management?
Projects often involve many tasks and team members. Without a clear plan, it becomes hard to know which delays really matter. CPM brings clarity by highlighting the most time-sensitive tasks. It is used because it helps:
1) Set realistic deadlines
2) Identify scheduling risks early
3) Allocate resources effectively
4) Monitor project performance
5) Make informed decisions when delays occur
Instead of guessing which tasks are important, CPM in Project Management uses logic and calculations. It shows exactly which activities control the project’s finish date. This makes planning more accurate and less stressful.
Benefits of Using CPM in Project Management
The Critical Path Method in Project Management offers practical, real-world benefits. It is not simply a theoretical framework, but a hands-on tool that supports planning, execution, and control. Let's check its benefits:
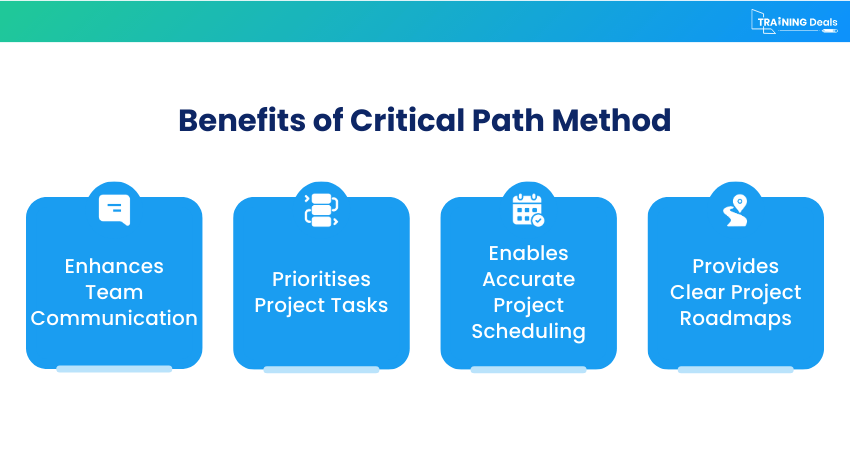
1) CPM Enhances Team Communication
One of the key benefits of using the Critical Path Method in Project Management is improved team communication. When the project schedule is clearly mapped and the Critical Path is identified, every team member understands how their work connects to the overall timeline. This reduces confusion about priorities and deadlines.
2) CPM Prioritises Project Tasks
The Critical Path Method helps Project Managers clearly identify which tasks must be completed on time to avoid delaying the entire project. By distinguishing between critical and non-critical activities, CPM ensures that attention and resources are directed toward the most important work. It allows allocating time, budget, and effort more strategically.
3) CPM Enables Accurate Project Scheduling
CPM improves the accuracy of project schedules by analysing task durations and dependencies in a structured way. Instead of loosely estimating timelines, it calculates the minimum time required to complete the project based on logical task sequences. This structured approach reduces guesswork and helps create real, achievable deadlines.
4) CPM Provides Clear Project Roadmaps
By mapping all activities in a network diagram, CPM offers a clear visual representation of the entire project. This roadmap shows how tasks connect, which ones run in parallel, and which ones directly impact the finish date. Thus, a clear roadmap makes planning, monitoring, and reporting much easier.
Enhance your decision-making and project control with PRINCE2® Practitioner Training – Register today!
How to Find and Calculate the Critical Path?
Now that you know what a Critical Path is and how it affects your project, it is time to explore how to find and calculate it. Below are the steps you can follow:
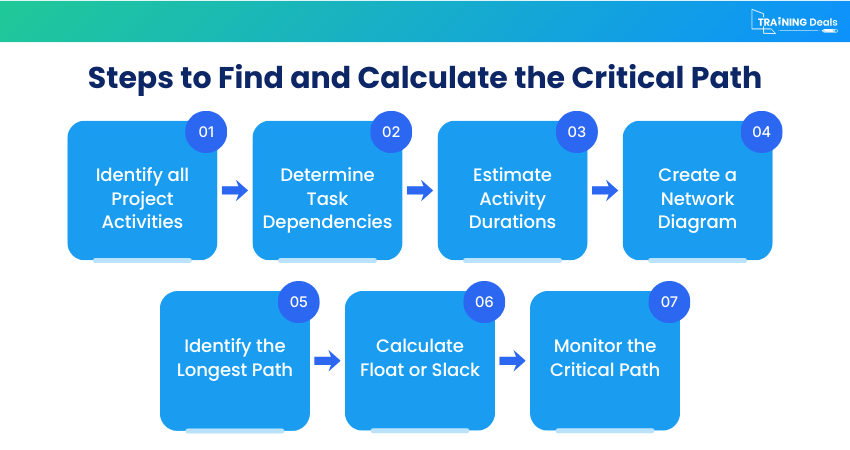
Step 1: Identify all Project Activities
The first step is to list every activity required to complete the project. This includes all major tasks and smaller supporting activities that contribute to the final outcome. A Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) is often used to ensure nothing important is overlooked.
Each activity should be defined with a specific deliverable with a start and an end point. You need to avoid vague descriptions such as “complete development” or “finish testing.”
Step 2: Determine Task Dependencies
After listing all project activities, the next step is to identify how these tasks are connected. Task dependencies show the order in which activities must be completed. Some tasks cannot begin until others are finished, while some may run at the same time.
Understanding these relationships is essential because dependencies shape the flow of the project. Common types include Finish to Start, Start to Start, Finish to Finish and Start to Finish.
Step 3: Estimate Activity Durations
Once task dependencies are clear, you need to estimate how long each activity will take to complete. These time estimates should be realistic and based on past experience, expert judgement, or historical project data.
Accurate estimates are important as they directly affect the overall project timeline. However, underestimating it can lead to schedule delays, while overestimating may create unnecessary slacks in the plan.
Step 4: Create a Network Diagram
After defining activities, dependencies, and durations, you need to create a network diagram. It is a visual representation of all the project activities and the relationships between them. Tasks are shown as nodes or boxes, while arrows indicate the direction of workflow and dependencies.
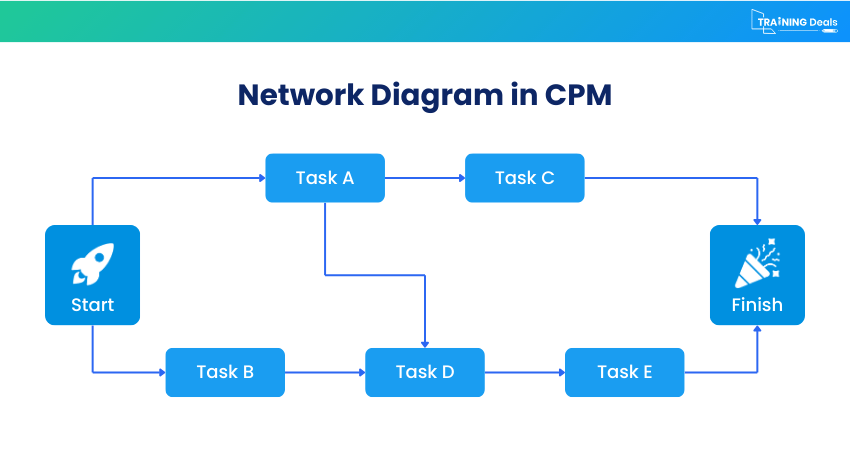
It helps identify parallel activities, detect potential bottlenecks, and calculate the Critical Path. It offers a clear picture of the project structure and supports accurate scheduling and planning.
Step 5: Identify the Longest Path
Now, you need to calculate the duration of each path from the start to the end of the project. This is done by adding the estimated durations of all activities within each sequence. The path with the longest total duration is known as the Critical Path.
Any delay in the activities on this path will directly impact the project completion date. Due to this, close monitoring and careful management are carried out.
Step 6: Calculate Float or Slack
Float, also known as slack, represents the amount of time a task can be delayed without affecting the overall project completion date. Tasks on the Critical Path typically have zero float, meaning they cannot be delayed at all.
To calculate float, Project Managers compare the earliest and latest start and completion times for each activity. The difference between these times shows how much flexibility a task has.
Step 7: Monitor the Critical Path
Identifying the Critical Path is not the final step. It needs to be monitored continuously throughout the project lifecycle. As work progresses, delays, early completions, or changes in scope can shift the Critical Path and affect the overall timeline.
Regularly reviewing task progress and updating the schedule ensures that critical activities remain on track. This helps respond quickly to issues and adjust resources when necessary.
Start your journey towards flexible Project Management with PRINCE2 Agile® Foundation Course – Join soon!
How to Use the Critical Path Method?
Understanding how to identify the Critical Path Method is important. But it is necessary to know how to use them effectively for your projects. Here is how you can use CPM:
1) Schedule Compression Techniques
When a project is running behind schedule or needs to be completed sooner, Project Managers may use schedule compression techniques to reduce project duration without changing scope. It can be done in two ways:
1) Crashing: Adding extra resources to critical tasks to reduce their duration and complete them faster.
2) Fast Tracking: Performing tasks in parallel that were originally planned to be done one after another.
Both techniques carry risk and may increase costs. However, when applied strategically to Critical Path activities, they can help recover lost time.
2) Managing Resource Constraints
Resources like skilled employees, equipment, and budget are often limited in a project. The Critical Path Method helps managers use these resources properly by focusing on the tasks that directly affect the project’s deadline.
Resource levelling ensures that workloads are balanced without overburdening individuals. In some cases, resource constraints may create a new Critical Path. This highlights the importance of reviewing schedules regularly.
3) Using CPM for Ongoing Project Control
CPM is also a powerful monitoring tool during project execution. By tracking progress on critical activities, Project Managers can quickly identify delays that may affect the final completion date. It acts as a control mechanism for your project execution process.
Regular updates to the schedule ensure that any changes in task durations or dependencies are reflected accurately. This allows managers to take corrective actions early, minimise risks, and keep the project aligned with its planned timeline.
Limitations of Critical Path Method
The Critical Path Method is very helpful, but it also has some drawbacks. Knowing these limitations helps you plan accordingly:
1) Depends on Accurate Information: CPM relies on correct task durations and dependencies, and because of this, inaccurate data leads to unrealistic schedules.
2) Focuses Mainly on Time: CPM concentrates mostly on schedule management. It does not directly manage cost, quality, or scope, so these areas must be controlled using other tools.
3) Not Very Flexible: CPM works best when the project plan is stable. It can feel rigid in fast-changing projects, requiring frequent updates when plans change.
4) Limited Resource Consideration: CPM in Project Management mainly focuses on task order and time. It does not automatically check if enough employees, equipment, or budget are available.
5) Can Be Difficult for Large Projects: In big or complex projects, the network diagrams can become complicated and hard to manage. Without Project Management software, updating and calculating the schedule can take a lot of time.
6) Needs Regular Updates: The Critical Path can change as the project moves forward. If the schedule is not updated regularly, it may no longer reflect the real situation, reducing its usefulness.
Conclusion
The Critical Path Method in Project Management is one of the most effective tools for managing project schedules. It brings clarity to complex projects, highlights the most important time-critical tasks, and helps managers make better decisions. When combined with realistic planning, regular updates, and proper resource management, it becomes a powerful method for delivering projects on time and with greater clarity.
Strengthen your project leadership skills with PRINCE2® Training – Begin now!
Search
- PRINCE2 vs APM: A Complete Guide to their Differences
- 10+ Project Management Tools to Boost Productivity in 2026
- What is Scrum? Agile Framework Explained
- What is Project Management? Phases, Approaches, and Benefits
- What is Agile Project Management? A Comprehensive Guide
- What are Project Management Skills: Top 25+ Skills You Must Know
- AI in Project Management: Benefits, Challenges, and Best Practices
- What is Project Management Triangle? Key 3 Constraints Explained
No match found
Latest Blog
AI in Project Management: Benefits, Challenges, and Best Practices
February 07, 2026
What is the Critical Path Method in Project Management? Explained
February 12, 2026
What is Project Management Triangle? Key 3 Constraints Explained
February 13, 2026
What are Project Management Skills: Top 25+ Skills You Must Know
February 06, 2026





















