

Richard Harris
Great projects do not happen by chance. They succeed because of clear planning, strong coordination, and a well-defined approach to managing work. In a world where deadlines are tight and expectations are high, having a structured way to manage work is essential. That's possible when you have effective Project Management. But What is Project Management?
This blog will explain it. Project Management provides the structure, tools, and techniques that help teams deliver successful projects, manage risks, and use resources effectively. This blog discovers What is Project Management, its key phases, approaches, and the benefits it brings to modern organisations. So, let’s get started!
What is Project Management?
Project Management is the process of planning, organising, and managing work in a project to achieve a specific goal within defined time, scope, and budget constraints. A project has a clear beginning and end, created to deliver a unique product, service, or result. Project Management ensures that this effort is executed in a structured and controlled way.
It typically involves defining the project scope, setting clear objectives, planning and sequencing tasks, assigning roles and responsibilities, managing risks, monitoring progress, and formally closing the project once the intended goals are achieved. When applied effectively, Project Management helps teams stay aligned, minimise risks, and deliver successful outcomes.

Why is Project Management Important?
Project Management is important because it brings structure and clarity to complex work. Without it, projects often face delays, rising costs, unclear goals, and unhappy stakeholders. Here are more reasons that justify why it is important:
1) Clear Direction and Goals: Project Management ensures everyone understands project objectives, scope and individual responsibilities, keeping the team focused and aligned.
2) On-time and On-budget Delivery: Proper planning helps avoid delays, cost overruns, and last-minute pressures.
3) Effective Risk Management: Risks are identified early and managed before they cause major issues.
4) Strong Communication: Clear communication keeps teams and stakeholders aligned with the project goals.
5) Efficient Resource Use: Resources such as people, tools, and materials are planned and used wisely, reducing waste and overload.
6) Improved Quality Outcomes: By setting clear standards and review processes, it improves deliverable quality.
7) Better Decision-making: Accurate tracking and performance data help with informed decision-making.
Who Uses Project Management?
Project Management is used across industries, roles, and organisational levels. It is not limited to Project Managers or large enterprises. Anyone responsible for delivering work with a defined goal can benefit from Project Management principles. Here's a list of who uses it:
1) Project Managers and Team Leaders: These professionals use Project Management to plan work, coordinate teams, and deliver objectives successfully.
2) Businesses and Organisations: Companies use Project Management to manage change, improve processes, and deliver strategic initiatives.
3) Construction and Engineering Teams: Project Management helps manage complex schedules, safety requirements, and large budgets.
4) IT and Software Development Teams: It supports system development, upgrades, and digital transformation projects.
5) Marketing Teams: Marketing teams use Project Management to plan campaigns, manage timelines, and coordinate creative efforts.
6) Product and Service Development Teams: Project Management supports the design, development, and launch of new products and services.
7) Healthcare and Education Sectors: Hospitals and institutions use Project Management to improve services, implement systems, and manage programmes.
8) Small Businesses and Startups: Entrepreneurs use Project Management to launch products, manage clients, and grow operations.
9) Individuals and Freelancers: Individuals apply Project Management skills to organise their personal goals, events, and freelance work.
Project Management Approaches
Project Management approaches describe how a project is planned, executed, and delivered. Different projects require different approaches depending on factors such as complexity, uncertainty, and stakeholder needs. Below are the most common Project Management approaches:
1) Predictive Project Management
Predictive Project Management follows a fixed plan. The scope, schedule, and cost are decided early in the project. The project's progress is measured against this plan, and changes are carefully controlled.
This approach works best when requirements are clear from the start and unlikely to change. Examples include building construction, manufacturing, and legal or compliance projects.
2) Adaptive Project Management
Adaptive Project Management is designed for change. Instead of planning everything in detail at the beginning, work is delivered in small parts. Feedback is gathered regularly, and plans are adjusted as needed.
This approach is common in software development and digital projects where customer needs may change over time. Teams learn as the project starts and improve the product step by step.
3) Hybrid Project Management
Hybrid Project Management combines predictive and adaptive approaches. It allows teams to use structure where needed and be flexible without predefined structure whenever required. These approaches are popular because they reflect how real projects work today.
This approach is commonly used in complex business, IT, and transformation projects where a balance between control and adaptability is essential.
Prove your expertise in managing projects effectively with PRINCE2® Practitioner Training – Register today!
Phases of the Project Management Life Cycle
Project Management involves a life cycle to manage a project from start to end. Here are the phases involved in its life cycle:
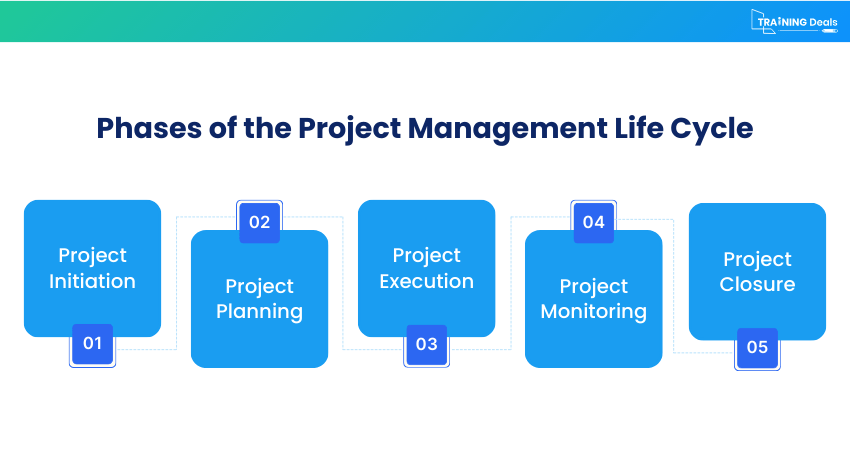
1) Project Initiation
The initiation phase is where the project begins. The goal is to understand the project’s purpose, objectives, and feasibility. Key stakeholders are also identified, and initial approval is sought. Strong initiation helps ensure that the project is worth doing and aligned with business goals.
Key Elements to Prepare:
1) Business case or project justification
2) Project charter
3) Initial stakeholder identification
4) High-level project objectives
5) Feasibility and approval documents
2) Project Planning
Planning is one of the most important phases of the Project Management life cycle. It involves deciding how the work will be done. The project tasks are defined, timelines are created, costs are estimated, and risks are identified. This phase also involves creating plans for communication, quality, and product purchasing when needed.
Key Resources Required:
1) Project scope statement
2) Detailed project schedule and milestones
3) Budget and cost estimates
4) Risk management plan
5) Resource allocation plan
3) Project Execution
The execution phase is where the planned work is carried out and put into action. Tasks get completed, deliverables are produced, and teams collaborate to move the project forward. The Project Manager coordinates the project activities, supports the team, and resolves any issues that arise.
Key Elements to Include:
1) Project team and assigned roles
2) Task and activity management tools
3) Communication and collaboration tools
4) Quality assurance processes
5) Issue and change management logs
4) Project Monitoring
The monitoring phase runs alongside project execution. It focuses on tracking progress and project performance. Key metrics such as schedule, cost, scope, and quality are reviewed regularly. If problems appear, corrective actions are taken. This helps keep the project on track and avoids bigger issues later.
Key Resources to Use:
1) Performance tracking metrics
2) Progress reports and status updates
3) Risk and issue registers
4) Schedule and budget tracking tools
5) Change control processes
5) Project Closure
The closure phase is the end of the project. Deliverables are handed over, documentation is completed, and stakeholders confirm acceptance of outcomes. The team reviews what went well and what could be improved. The feedback is documented for future projects.
Key Documents to Maintain:
1) Final deliverables and approvals
2) Project completion report
3) Lessons learned documentation
4) Stakeholder sign-off
5) Resource release and handover documents
5 Project Management Methodologies
There are different ways to manage a project. Let's check some of the most common Project Management Methodologies:
1) Agile Project Management
Agile Project Management focuses on incremental delivery, flexibility, and collaboration. Work is broken into small iterations, often called sprints, with regular feedback from stakeholders. Agile encourages continuous improvement and quick adjustments when there are changes in the project delivery.
Best Used for:
1) Projects with changing or unclear requirements
2) Software and digital product development
3) Customer-focused and feedback-driven work
4) Fast-moving and innovative environments
Understand how to manage Agile projects with PRINCE2 Agile® Foundation Training – Join now!
2) Lean Project Management
Lean Project Management aims to maximise value while minimising waste. Lean principles encourage teams to identify non-value-adding activities and eliminate them. This leads to faster delivery, lower costs, and improved quality. This also focuses on project efficiency, simplicity, and continuous improvement.
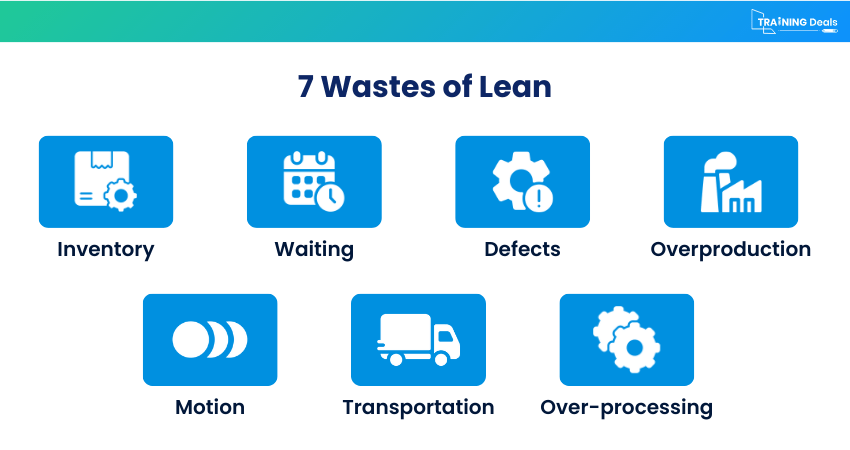
Best Used for:
1) Process improvement initiatives
2) Cost reduction and efficiency-focused projects
3) Manufacturing and operations environments
4) Projects aiming to reduce waste
3) Waterfall Project Management
Waterfall Project Management is a traditional, sequential methodology that follows a step-by-step approach. Each phase of the project must be completed before the next phase begins. Project requirements are defined upfront, and changes are minimal once execution starts.
Best Used for:
1) Projects with clear and fixed requirements
2) Construction and infrastructure projects
3) Regulatory or compliance-based work
4) Projects requiring detailed documentation
4) Kanban Project Management
Kanban Project Management focuses on visualising work and managing flow. In this, all tasks are displayed on a board, typically using columns such as to do, in progress, and completed sections. This approach helps teams identify bottlenecks and improve workloads. It supports continuous delivery rather than fixed phases or iterations.
Best Used for:
1) Ongoing work with continuous delivery
2) Teams needing clear task visibility
3) Workload and flow management
4) Support and operational teams
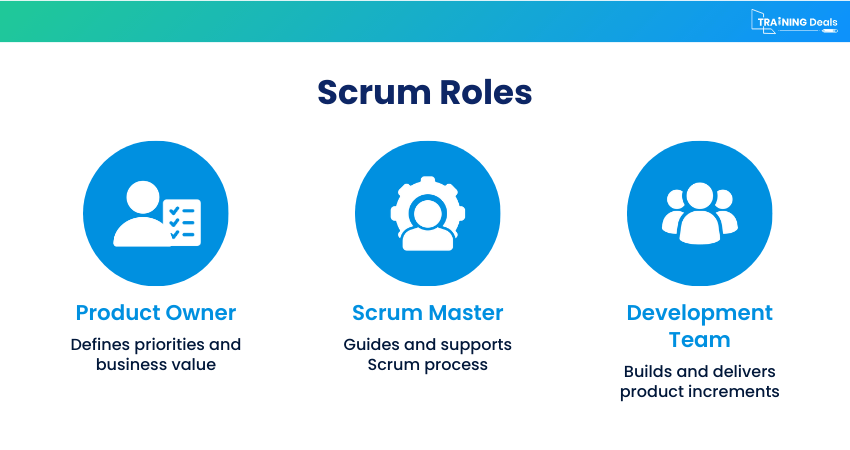
5) Scrum Project Management
Scrum Project Management focuses on delivering work in short, fixed time periods called sprints. Scrum, as an Agile framework, uses defined roles such as the Product Owner, Scrum Master, and Development Team to ensure clarity and accountability. This approach is highly effective for complex projects where requirements evolve and fast; flexible delivery is essential. Regular reviews and feedback help teams adapt quickly and deliver value incrementally.
1) Software and application development
2) Projects with changing requirements
3) Cross-functional and collaborative teams
4) Products that need frequent updates and feedback
What are the Benefits of Project Management?
Project Management comes with a lot of benefits for businesses and individuals. The following are its benefits:
1) Provides clear goals, roles, and responsibilities for everyone involved
2) Improves project planning, scheduling, and task prioritisation
3) Reduces risks by identifying and managing issues early
4) Ensures better use of resources, time, and budget
5) Improves the quality of deliverables through defined standards
6) Increases customer and stakeholder satisfaction
7) Improves overall project success rates
Build confidence in managing Agile projects with PRINCE2 Agile® Foundation and Practitioner Training – Sign up soon!
What Tools are Used in Project Management?
If you want to implement an effective and strong Project Management, there are some tools you can use. They help teams plan, organise, track, and control project activities more effectively. Below are some of the tools you can check out:
1) Project Dashboard
A project dashboard is a visual summary that displays important project information in one place. It shows details such as progress, deadlines, risks, and performance indicators, helping managers and stakeholders quickly understand the overall details of a project.
Key Features:
1) Real-time project status updates
2) Visual indicators such as charts and graphs
3) Key performance metrics and milestones
4) Risk and issue highlights
5) High-level overview for stakeholders
Tips to Consider:
1) Focus only on key metrics that matter to the project
2) Keep the dashboard simple and easy to understand
3) Update data regularly for accuracy
4) Customise views for different stakeholders
2) Gantt Charts
Gantt charts are visual planning tools that display project tasks along a timeline. They show when tasks start and end, how tasks are connected, and which activities depend on others, making it easier to plan schedules and track progress.
Key Features:
1) Task timelines and durations
2) Task dependencies and sequencing
3) Start and end dates
4) Milestones and deadlines
5) Progress tracking
Tips to Consider:
1) Break tasks into manageable activities
2) Define clear task dependencies
3) Set realistic timelines and deadlines
4) Review and adjust the chart when changes occur
3)Kanban Boards
Kanban boards are visual workflow tools that organise tasks into columns such as To Do, In Progress, and Completed. They help teams track work, manage workloads, and improve flow by clearly showing the status of each task.
Key Features:
1) Visual task cards
2) Customisable workflow columns
3) Work-in-Progress (WIP) limits
4) Easy task movement between stages
5) Improved visibility and transparency
Tips to Consider:
1) Keep workflow stages clear and simple
2) Limit Work-in-Progress to avoid overload
3) Update task status regularly
4) Review the board frequently to improve flow
Tips for Successful Project Management
To have a successful Project Management, here are the tips that you can follow:
1) Define a Realistic Project Scope
Clearly explain what the project includes and what it does not. This helps avoid confusion and prevents extra work from being added later.
How to Follow it:
1) Clearly list what work is included in the project
2) Mention what is not part of the project
3) Get agreement from stakeholders before starting
4) Avoid adding new tasks without review
2) Prioritise Effective Scheduling
Create a schedule that is practical and easy to follow. This helps the team manage tasks on time without feeling rushed.
How to Follow it:
1) Break work into small, manageable tasks
2) Set realistic deadlines for each task
3) Identify task dependencies early
4) Review and update the schedule regularly
3) Actively Involve Stakeholders
Keep stakeholders involved throughout the project. Regular updates and feedback help ensure everyone stays aligned and informed.
How to Follow it:
1) Identify key stakeholders at the start
2) Share regular progress updates
3) Ask for feedback at important stages
4) Address concerns quickly
4) Invest Time in Initiation and Planning
Spend enough time on project planning before starting the work. Good planning helps avoid problems and makes the project run more smoothly.
How to Follow it:
1) Define clear project goals
2) Identify risks early
3) Create a simple project plan
4) Ensure the team understands the plan
5) Apply Efficient Resource Management Practices
Use people, time, and tools carefully. This helps reduce waste and prevents team members from being overworked.
How to Follow it:
1) Assign tasks based on skills and availability
2) Avoid overloading team members
3) Track resource usage regularly
4) Adjust resources when needed
6) Foster Transparency and Accountability
Encourage open communication and clear responsibility among your team and stakeholders. This helps track progress and ensures tasks are completed on time.
How to Follow it:
1) Clearly assign ownership for each task
2) Encourage open communication between teams
3) Track progress with transparency
4) Address issues honestly and at early stages
Conclusion
Project Management plays a key role in turning ideas into successful outcomes by providing clear structure, defined processes, and the right tools. It helps teams plan work effectively, manage risks, and stay focused throughout the project lifecycle. With a proper understanding of What is Project Management and its methodologies, you can deliver projects with confidence, meet stakeholder expectations, and succeed in today’s fast-paced environment.
Learn a structured and practical approach to project delivery with PRINCE2® Training – Begin your journey!





















